Holtgrewe, et al. “Multisite de novo mutations in human offspring after paternal exposure to ionizing radiation." Scientific reports (2018)
A genome-wide evaluation of the effects of ionizing radiation on mutation induction in the mouse germline has identified multisite de novo mutations (MSDNs) as marker for previous exposure. Here we present the results of a small pilot study of whole genome sequencing in offspring of soldiers who served in radar units on weapon systems that were emitting ionizing radiation. We found cases of exceptionally high MSDN rates as well as an increased mean in our cohort: While a MSDN mutation is detected in average in 1 out of 5 offspring of unexposed controls, we observed 12 MSDNs in altogether 18 offspring, including a family with 6 MSDNs in 3 offspring. Moreover, we found two translocations, also resulting from neighboring mutations. Our findings indicate that MSDNs might be suited in principle for the assessment of DNA damage from ionizing radiation also in humans. However, as exact person-related dose values in risk groups are usually not available, the interpretation of MSDNs in single families would benefit from larger molecular epidemiologic studies on this new biomarker.
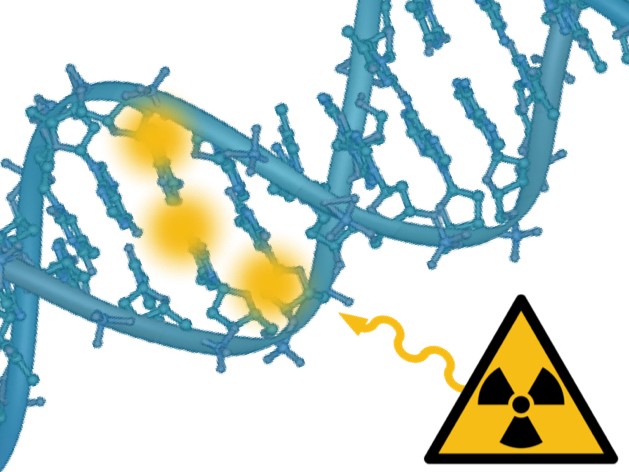
Illustration of radiation altering the genome: a ‘multisite de novo mutation’ (MSDN) occurs when two or more defects occur adjacently in the DNA strands of 20 base pairs.(c) 2018 Institute of Genomic Statistics and Bioinformatics/UKB
Follow-Up Study
Note that we are performing a follow-up study together with Universität Bonn funded by the German Ministry of Defense. Additional information can be found on the Radar Study homepage
Press Releases
- Typische Mutationen bei Kindern von Radarsoldaten - Press Release Universität Bonn
- Typical mutations in children of radar soldiers - Press Release Universität Bonn
- Typische Mutationen bei Kindern von Radarsoldaten - Press Release Berlin Institute of Health
- Typical mutations in children of radar soldiers - Press Release Berlin Institute of Health
Media Coverage
Last modified: Mar 21, 2024